Sample data generation
The Sample-data generation is the process of generating fake, but as much as realistic as possible, measurements associated to the mock Basket.
The “mock Basket” is a special Basket used for tests that is characterized by the ID 0x23232323 in hex, or 589505315 in decimal.
The problem consist in generating three type of measurements:
- Accelerometer data: the movement of the Basket or of the Basket board above a certain threshold.
- People detection data: the detection of people standing in front of the basket.
- Basket data: anything that occluded the IR detector (most commonly, the ball entering the basket).
The task of the generator, given a range of dates, is to generate for each day within the range fake measurements.
In order to do this, the generator distinguish three types of days in a year:
- Busy day: a day for example of school or of work.
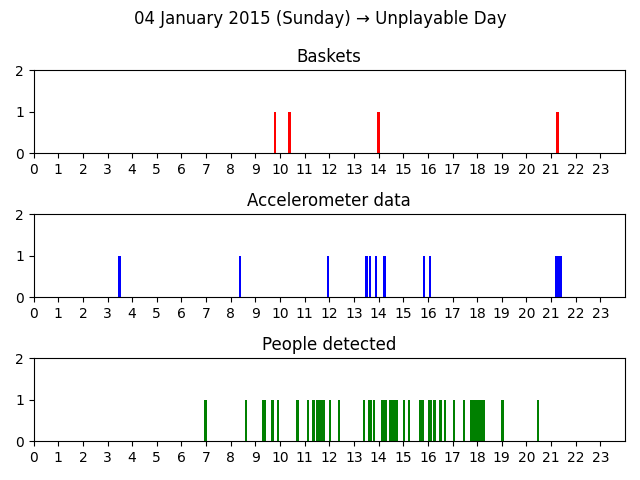
- Unplayable day: a day that is considered to be unplayable for example because of bad weather conditions (rain or cold).
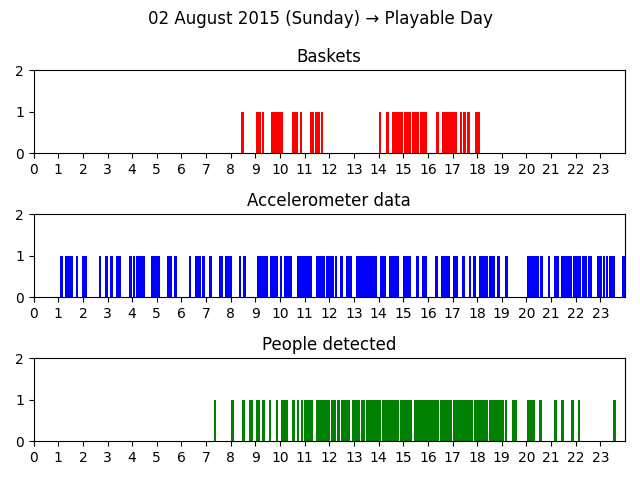
- Playable day: any other day.
For every day type and for every measurement type, it’s built a probability distribution from which the generator will sample pseudo-realistic timestamps for the measurement.
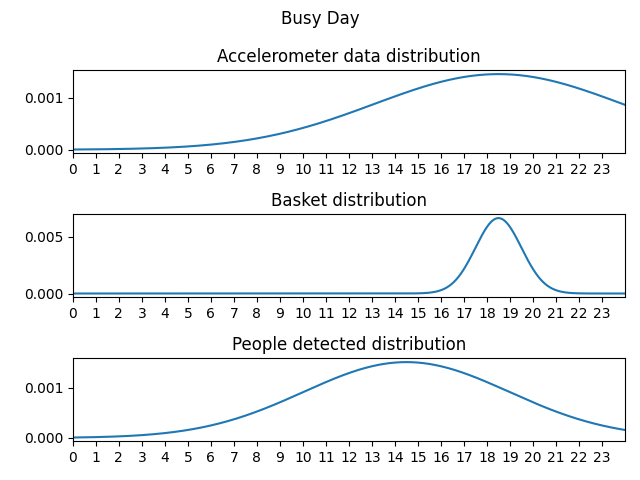
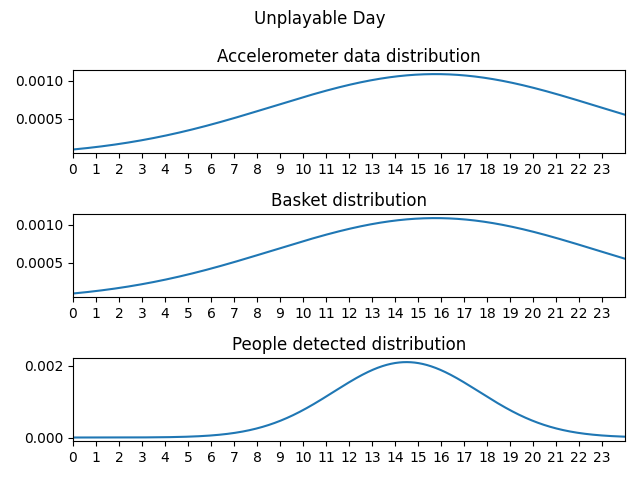
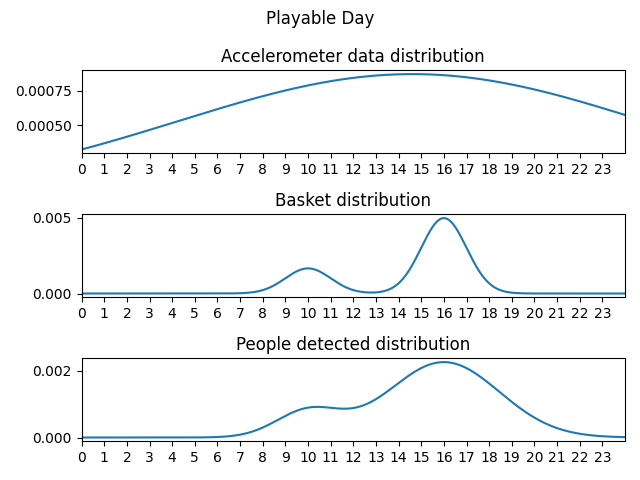
Even the number of timestamps drawn within a day per measurement are dependent on the day type. Trivially it’s expected to have more baskets, people detected and accelerometer data on a Playable day rather than on an Unplayable day.
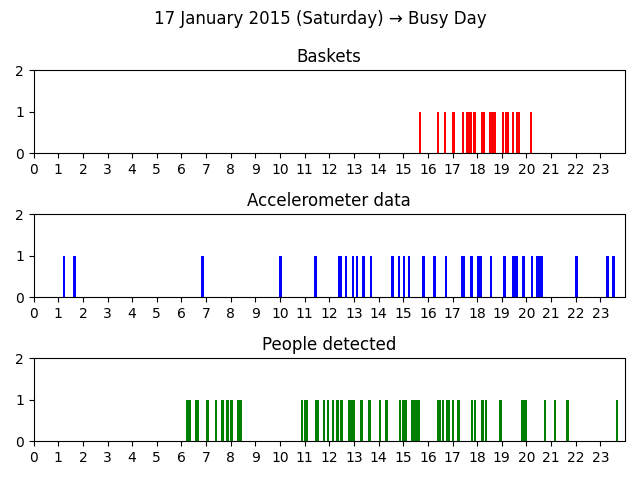
How a day is classified?
A date is classified using the following procedure:
- If a day is unplayable then it’s Unplayable
- Otherwise the day is playable, but if it’s busy, then it’s Busy
- Otherwise it’s Playable
Unplayable day classification
The condition for a day to be unplayable should be derived from realistic weather data. However we don’t have access to a weather service that could give us the exact weather conditions back in the past and its integration would have been an over-engineering for the generation of sample fake-data.
For this purpose, it’s been implemented a predicate that given a date returns whether the day was playable or unplayable. This predicate has to be deterministic, thus the day condition can’t involve a random generator. The randomness has been replaced with a noise function that given a numerical representation of the date (e.g. Unix timestamp) returns a [0, 1] value. This value is then converted to a boolean value giving more probability to autumn/winter month’ days to be unplayable and less to spring/summer days.
def noise(n: float):
return abs(modf(sin(n) * 43758.5453123)[0])
def is_unplayable_day(date: datetime):
value = noise(mod(date.year, 5) * 365 + date.month * 31 + date.day)
return value <= [0.9, 0.8, 0.6, 0.38, 0.3, 0.1, 0.08, 0.07, 0.1, 0.3, 0.79, 0.9][date.month - 1]
Busy day classification
A day is considered busy trivially if respects these hand-crafted conditions:
- The month is within school period (January to May or September to December)
- It’s not a Sunday
- It’s not Christmas holiday